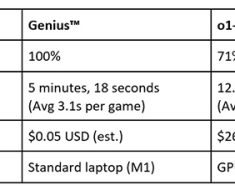
Artificial Intelligence (AI) technology is revolutionizing many sectors, and healthcare is no exception. Among the AI technologies making waves is the Large Language Models (LLMs). These models, combined with real-time analytics, are disrupting traditional healthcare workflows and paving the way for more efficient, personalized patient care. Benjamin Wootton, the Founder & CTO of Ensemble, recently demonstrated this technology in action, revealing its potential impact on the payments and financial crime space.
Understanding Large Language Models
Large Language Models (LLMs) are AI algorithms trained on extensive amounts of text data to create natural language outputs. These models, which sound as legitimate as human-written text, have become increasingly popular in recent years, especially in the field of natural language processing (NLP). The advent of transformers, a deep learning structure that uses attention mechanisms to handle sequential data like text, has significantly improved the NLP field, achieving the best performance in various challenges. LLMs leverage pre-training on large amounts of data and fine-tuning specific tasks to understand and generate human-like text. They excel in natural language processing tasks including language generation, text completion, and question answering. However, they also come with challenges such as data bias, fairness, privacy, and sustainability.
LLMs in Action
The demo conducted by Wootton showcased the use of real-time transaction data in an interactive application, where a large language model asks questions about the data in real-time. This demonstrates the ability of LLMs to interact with real-time data and generate pertinent insights. The demo also explored the use of Generative AI to make the agent more efficient, automating workflows such as customer communications. This can significantly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare workflows, from scheduling patient appointments to answering patient queries and more.
Real World Use Cases
The demo further showcased the use of LLMs like ChatGPT and Anthropic via AWS Bedrock with ClickHouseDB, demonstrating real-world RAG use cases. These models are not only advancing AI systems capable of understanding and generating human language but are also making website creation, maintenance, and monetization more accessible for those without technical skills. Some top large language models of 2024 include the Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) 3.5 and GPT 4 from OpenAI, and BARD from Google AI. Each model offers unique capabilities for website creation, monetization, and marketing.
Unlocking LLM Potential
LLMs powered by deep learning techniques, such as OpenAI’s GPT series, have revolutionized natural language understanding and hold immense potential for various industries, including healthcare. They enable machines to comprehend and interpret human language more effectively than ever before by analyzing vast amounts of text data. However, ethical concerns tied to LLMs include privacy, bias, misinformation, and the environmental impact of their computational resources. Despite these challenges, the potential of LLMs in transforming healthcare operations and patient care is undeniable.
LLM-Based Model Development
Building an LLM model requires a massive dataset of text and code, a powerful computer, and a deep learning framework. These models are designed to process and generate human language with a high level of fluency and coherence. They are trained on vast amounts of text data and operate through pre-training and fine-tuning processes. Pre-training involves unsupervised learning to absorb linguistic patterns and contextual cues, while fine-tuning makes the model more task-specific. Prompt tuning further guides the model for specific tasks. Once trained, LLMs can be deployed for practical applications across various industries, including healthcare.
In conclusion, the combination of Large Language Models (LLMs) with real-time analytics holds immense potential for transforming healthcare practices. From automating routine tasks to enhancing patient communication, the possibilities are endless. While challenges persist, the benefits offered by these models far outweigh the drawbacks, making them a promising tool for the future of healthcare.