It’s been a decade since NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang delivered the company’s DGX AI supercomputer to Open AI, and at CES 2024 in Las Vegas, the smart robotics organization made another major announcement in the artificial intelligence and robotics field.
Speaking in a special address at CES, NVIDIA Vice President of Robotics and Edge Computing Deepu Talla laid out a plan for the company and its partners – including Boston Dynamics, Covariant, Sanctuary AI, Unitree Robotics, Collaborative Robotics and others – to bring generative AI and robotics together.
At the center of the relationship is GPU-accelerated large language models (LLMs), which bring higher levels of adaptability and intelligence to various machines.
The “human” brain of robotics
LLMs work as the language center in the robot “brain” and will allow them to better understand and more naturally respond to human prompts. As such, these machines will have the ability to learn from not only human interaction, but their robot counterparts.
“Given these attributes, generative AI is well-suited for robotics,” Talla said.
Dual-computer model for deploying AI in robotics
As part of Talla’s talk at CES, he demonstrated how NVIDIA’s dual-computer model is essential for deploying AI in robotics.
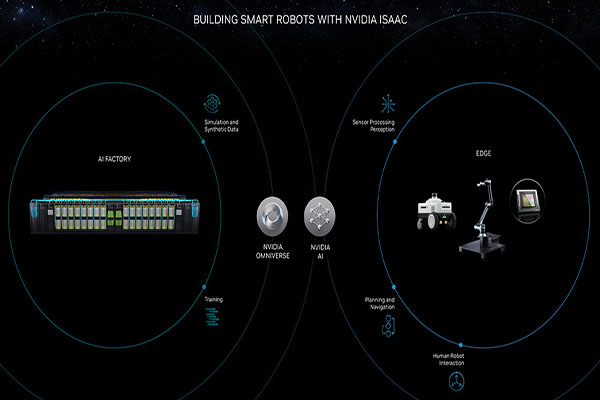
NVIDIA’s Isaac platform and its dual-brain model.
In this model, the first computer, referred to as the “AI factory” plays a major role in the creation and continual improvements of AI models.
Organizations can use NVIDIA’s data center compute infrastructure in conjunction with its AI and NVIDIA Omniverse platforms to simulate and train AI models.
The second computer in the model represents the robot’s runtime environment, whether that’s on the cloud or in a data center.
LLMs help break down technical barriers
Another element Talla mentioned as part of his presentation was the ability of LLMs to reduce techincal barriers with users. He described how typical users of a robot can use it’s LLM through prompts and training and morph into a technical artist capable of creating complex robotics workcells or entire warehouse simulations.
NVIDIA Picasso allows users to generate realistic 3D models from simple text prompts and add them to digital scenes for robot training environments. Users can also use this capability to create diverse and physically accurate scenarios in Omniverse to enhance robotic training and ensure real-world applicability.
Instead of robots being built for specific tasks and spending countless hours modifying them for other ones, the hope is that these advancements in LLMs and vision language models will reduce those bottlenecks and allow for better human-robot interactions through natural language, Talla said.
Robots using generative AI
Across various industries, robots are using generative AI to help them understand text or voice commands. Agility Robotics, NTT and robot vacuum cleaners from Dreame Technology represent a small sample of organizations using generative AI in their robotic products.
About the Author
Tim CulverhouseTim is the Editorial Director of Robotics247.com. His mission is to provide valuable information and insights to robotics professionals and decision-makers, and to help them solve business challenges. He is a creative, deadline-driven, and detail-oriented storyteller. In addition, he is a sports broadcaster and public address announcer.
Follow Tim:
Follow Robotics 24/7 on Facebook
Follow Robotics 24/7 on Linkedin
Email Sign Up

Get news, papers, media and research delivered
Stay up-to-date with news and resources you need to do your job.
Research industry trends, compare companies and get market intelligence every week with Robotics 24/7.
Subscribe to our robotics user email newsletter and we’ll keep you informed and up-to-date.





